WEB IProcess Pyme LITE!
Ideal for small companies that need productive modules, 10 corporate emails, 5 sections, 20 product catalog, 5 SEO campaigns, e-commerce.

 Español
Español
 English
English
Business Process Management (in English: Business Process Management or BPM) is a management discipline composed of methodologies and technologies, whose objective is to improve the performance (efficiency and effectiveness) and the optimization of the processes of an organization, equal to through the management of the processes that must be designed, modeled, organized, documented and optimized continuously. Therefore, it can be described as a process of continuous improvement of processes.
The process management model refers to the operational change of the company, when migrating from a functional operation to an operation managed by processes.
BPM is the understanding, visibility, modeling and control of the business processes of an organization. A business process represents a discrete series of activities or task steps that can include people, applications, business events, tasks, and organizations.

BPM can be related to other process improvement disciplines such as Six Sigma. Business processes should be documented (up-to-date), to help the organization understand what they are doing through their business.
During the process discovery stage, everyone is relatively in agreement on how the current processes are defined. The AS-IS determines the state where the information can be used to determine where the process should be improved, to arrive at a TO-BE, describing how the process should be. Documenting the process alone is not the tool for managers to take control over the entire process. BPM considers process monitoring essential to determine if the process generates the expected results based on the business objectives. The creation and use of metrics and KPIs is key to carry out detailed control of each process.
It was from the 80s when, as a result of the Japanese model (Toyota production system) and the appearance of mainly international quality standards, when the implementation of a structural system based on process management was promoted.
Previous approaches treated processes, people, and technology separately, creating a sometimes insurmountable gap between technologies and the organization`s business. This gap in the medium / long term results in losses (millions of dollars in many cases) that companies must face. An organization is regulated by processes, and it is these that make the organization have a life, which may be shorter or longer, depending on how they are implemented and the purposes they serve. If a company knows its processes, then it will be able to model them, study them, measure them, optimize them to satisfy the business objectives, and eventually change them as the activity evolves, when new opportunities appear, when certain technology becomes obsolete, etc.
The process management system is characterized by the understanding, visibility and control of all the processes of an organization by all the participants in each of these processes, all in order to increase the efficiency of the company and customer satisfaction.
Tools
To support this strategy, it is necessary to have a set of tools that provide the necessary support to comply with the BPM life cycle. This set of tools is called Business Process Management Software (BPMS), and with them BPM applications are built. They usually follow a common notation, called Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN). Others have their own notation and are capable of generating code.
The "silo effect"
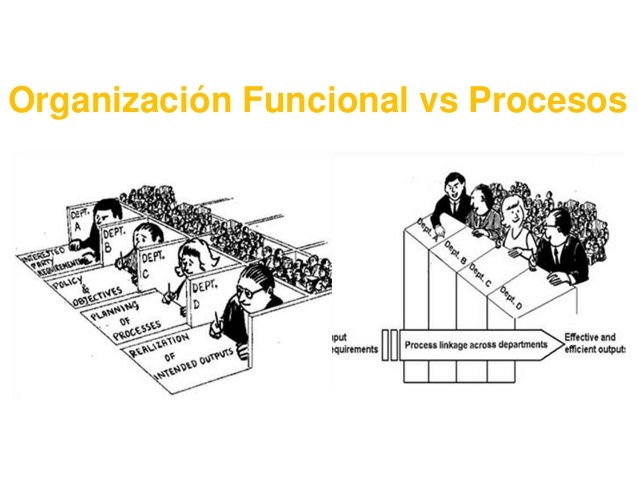
It is known as "silo effect" to a series of communication and priority-setting problems that usually occur in companies when they move from a traditional or functional organization to process management. This effect is opposed to a more comprehensive and general approach than that of the departmental structure, where the important thing is the process as a whole and not the interests of each department separately. A classic or department organization could be represented graphically as a vertical and segmented structure; while process-based management would be a set of horizontal and continuous lines.
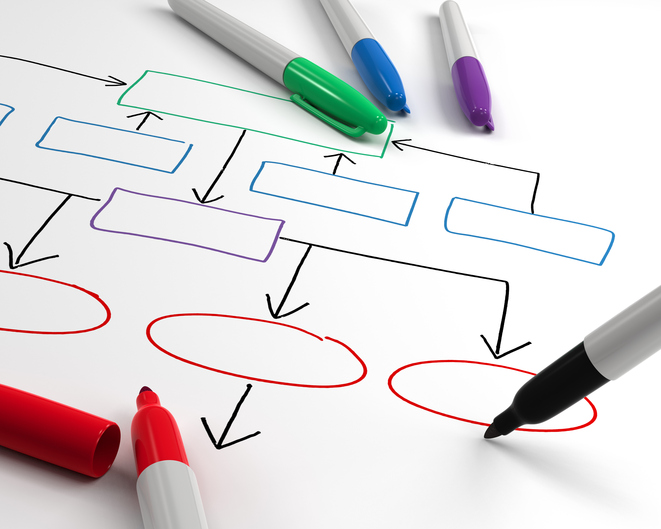
The value chain.
The value chain is a theoretical concept that describes the way in which actions and activities are developed in a company. This concept is highly relevant for process-based management, since it distinguishes different interrelated links in every production circuit. In this way, there would be primary activities, focused on the physical preparation of products and support actions, which do not provide value in themselves, but are not without importance for that. Process-based management takes into account the entire value chain as a whole and horizontally.
Myths of process automation
Automation of processes is something that almost every company wants to achieve to improve its operations, reduce costs and increase profits. The key issue that many forget is that before automating any process, it must first be understood and improved. It is well worth remembering the words of Bill Gates on this subject:
The first rule of thumb of any technology used in a business is that automation applied to efficient operation will magnify efficiency. The second is that automation applied to an inefficient operation will magnify the inefficiency.
Corollary: automation is useless if the process is not fixed or improved from a business point of view. Through BPM it is easier to understand processes, therefore model, understand and optimize them, and then implement subsequent automation. As previously mentioned, the joint vision of processes, people and technology, in order to improve the performance of processes is key to the success of any company.
Tips for implementing a process-based management system.
Have the commitment of the management to implement this management system.
Identify the processes that exist within your company and establish connections between them.
Complete a process mapping that helps employees visualize workflows and the new structure.
Carry out a pilot experience.
Publication Date: 2021-08-12
Source: euskalit.net

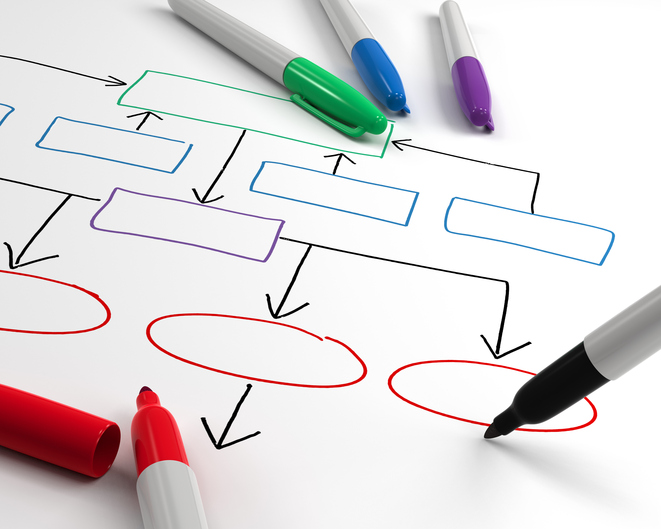




Ideal for small companies that need productive modules, 10 corporate emails, 5 sections, 20 product catalog, 5 SEO campaigns, e-commerce.

Ideal to start your presence on the internet, catalog of 5 products, updating documents, hosting, corporate emails and more!

Ideal for small companies that need productive modules, 10 corporate emails, 5 sections, 20 product catalog, 5 SEO campaigns, e-commerce.

Ideal to start your presence on the internet, catalog of 5 products, updating documents, hosting, corporate emails and more!