WEB IProcess Pyme LITE!
Ideal for small companies that need productive modules, 10 corporate emails, 5 sections, 20 product catalog, 5 SEO campaigns, e-commerce.

 Español
Español
 English
English
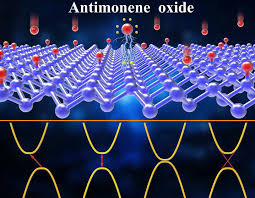
Recently, the news has emerged that a research group from the Autonomous University of Madrid has managed to isolate in the laboratory the two-dimensional material "antimonene", a material similar to graphene in structure, but composed of antimony atoms instead of carbon. This discovery opens the door to a large number of applications, especially in the energy field. We tell you a little more about this unusual material in this post.
Although its existence was already known thanks to theoretical studies, it has been in the last week when antimonene has managed to be isolated in the laboratory thanks to a research team from the Nanomaterials group of the UAM, in collaboration with the Sensors and Biosensors group of this same university, as well as with the group of experts in electrochemistry of the Manchester Metropolitan University of the United Kingdom. The discovery has been published in the scientific journal Advanced Energy Material.
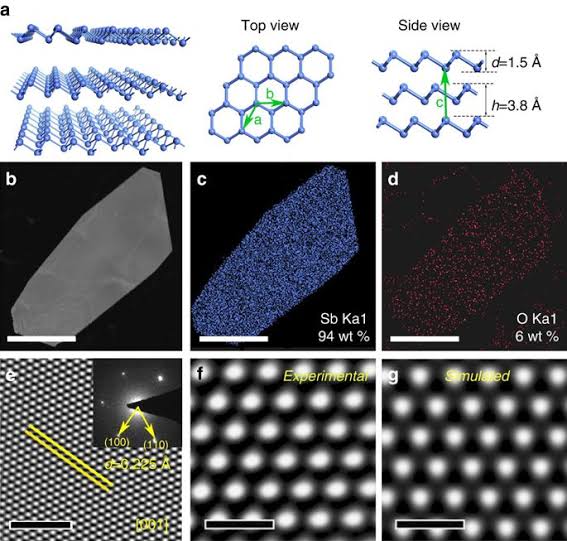
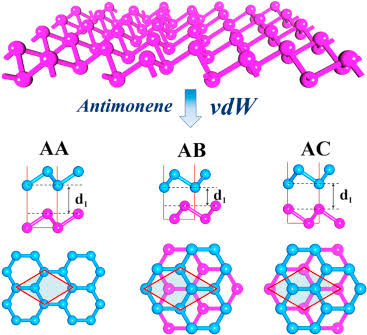
Among other characteristics, antimonene has a structure in the form of sheets of atomic thickness, similar to those of graphene but with antimony atoms instead of carbon, joining it in the list of so-called "two-dimensional materials" for its extraordinarily light thickness.
Since the synthesis of graphene more than a decade ago, the applications discovered for two-dimensional materials have been varied and are in the process of development today.
Among the contingent applications of antimonene, those in the field of energy generation and storage stand out, which are very favorable for the development of renewable energies, giving this good results when used in the manufacture of supercapacitors (devices capable of storing large quantities of electrical energy in the form of electrostatic charges). The operation of supercapacitors is based on the separation of electrostatic charges in the form of positive and negative ions thanks to the coating of the nanostructure of the antiomonene, either by anions or by cations.
According to the research carried out, antimonene is capable of storing four times more energy than graphene, also providing great stability in the face of electric energy charge-discharge cycles. These properties make it a strong candidate for application development within the energy field.
Another of the main characteristics of antimonene is its high surface / volume ratio, which facilitates the movement of ions inside it and makes it an ideal material for use in supercapacitors. This fact is also favored by the formation of channels and cavities between its nanometric sheets. The use of supercapacitors is increasingly widespread in replacement of cells and batteries, as well as in the electric motors of hybrid vehicles and also as emergency generators in the event of power outages in areas such as hospitals or elevators.
Likewise, applications of this material have begun to be investigated in elements such as long-life batteries for electronic devices or in the creation of sodium batteries, which can replace lithium batteries due to the scarcity of this. Everything indicates that antimonene will have a variety of applications as wide as graphene, but we will have to wait a while for the research and development of the relevant technology to discover others that we surely do not even imagine today.
Publication Date: 2020-01-01
Source: Blog. Structuralia. Com







Ideal for small companies that need productive modules, 10 corporate emails, 5 sections, 20 product catalog, 5 SEO campaigns, e-commerce.

Ideal to start your presence on the internet, catalog of 5 products, updating documents, hosting, corporate emails and more!

Ideal for small companies that need productive modules, 10 corporate emails, 5 sections, 20 product catalog, 5 SEO campaigns, e-commerce.

Ideal to start your presence on the internet, catalog of 5 products, updating documents, hosting, corporate emails and more!