WEB IProcess Pyme LITE!
Ideal for small companies that need productive modules, 10 corporate emails, 5 sections, 20 product catalog, 5 SEO campaigns, e-commerce.

 Español
Español
 English
English
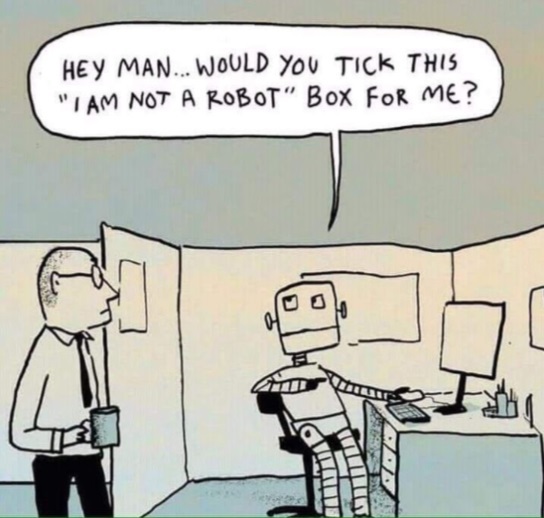
Has it happened to you that when you want to create an account on a website, you spend a good time trying to prove that you are a human being?
Before, all you had to do was press the "I`m not a robot" button or type in a window the sequence of letters that appears on the screen and seems submerged in water.
Now you must pass different tests, such as the one in which you are shown segmented images and you have to answer, for example, how many bridges, traffic signs or trees you see on them. But is what you see in the corner of the image a branch or the shadow of a pole?
The process is usually so complicated that you may feel that you are trying to pass a psychological test or a university admission test.
And it is all due to an automated system called Captcha that, in its advanced version, tests your ability to recognize invariable, segmentation and systematized analysis.
The process carried out successfully confirms your human status to the site and allows you to proceed, for example, with your purchase.
It is understandable that sites that offer goods and services want to avoid fraud, hacking and spam, but it is uncomfortable that artificial intelligence is demanding more and more demanding that you prove that you are not an automaton.
Where does Captcha come from?
The Captcha test is named after the "Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart".
Originally, this test was developed by British mathematician and computer scientist Alan Turing (1912-1954), who cracked the Enigma Code, the encryption of Nazi communications during World War II.
Turing created the test in the 1950s to determine if a computer was capable of thinking like a human.
Based on that test, computer experts from Carnegie Mellon University, in the United States, developed the Captcha system in the late 1990s, precisely to prevent people from programming automated robots to create fake accounts on websites.
Google bought it in 2009 to digitize books, a very useful tool for interpreting printed texts, but also for identifying people as human.
When a user logs into a website, they must prove they are human by solving visual puzzles that require them to identify letters, numbers, symbols, or objects that have been distorted or animated in one way or another.
Initially a robot had trouble solving questions that humans can easily analyze.
The problem is that artificial intelligence learns, and always faster, so the first tests lost their effectiveness.
A more humane test
That is why they have become increasingly difficult and, in that aspect, humans have it lost in front of machines.
In 2014, Google put one of its algorithm learning programs out there against humans, trying to solve the most distorted texts in Captcha.
The computer solved the test 99.8% of the time, while humans barely managed 33%.
An article on the computer science site The Verge suggests that much of the problem with Captcha tests is not that robots are so smart but that we humans are not very good at that type of test.
"Machine learning is now as good as humans in terms of text, image and speech recognition," says Jason Polakis, a professor of computer science at the University of Illinois at Chicago, quoted in The Verge.
"We`ve reached a point where by making things more difficult for hardware, we end up making things even more difficult for people. We need an alternative, but there is no concrete plan yet."
Polakis points out that the tests are limited by human ability, so something needs to be developed that includes cultural and language aspects. At the same time it has to be something that the human can solve quickly, without much hassle.
In other words, abandoning the Turing test to avoid a competition against machines that humans will continue to lose more frequently.
For that, Google has been developing the new generation of Captcha, called reCaptcha v3.
It combines the cookies we leave, the characteristics of the browser we use, traffic patterns and other elements to assess "normal" human behavior.
Everything, so that you do not have to differentiate a tree branch from the shade of an electric pole to be able to enter a website.
Publication Date: 2020-02-05
Source: BBC.com:



Ideal for small companies that need productive modules, 10 corporate emails, 5 sections, 20 product catalog, 5 SEO campaigns, e-commerce.

Ideal to start your presence on the internet, catalog of 5 products, updating documents, hosting, corporate emails and more!

Ideal for small companies that need productive modules, 10 corporate emails, 5 sections, 20 product catalog, 5 SEO campaigns, e-commerce.

Ideal to start your presence on the internet, catalog of 5 products, updating documents, hosting, corporate emails and more!