WEB IProcess Pyme LITE!
Ideal for small companies that need productive modules, 10 corporate emails, 5 sections, 20 product catalog, 5 SEO campaigns, e-commerce.

 Español
Español
 English
English
Autism spectrum disorder is a disease related to brain development that affects the way a person perceives and socializes with other people, causing problems with social interaction and communication.
The disorder also includes restricted and repetitive behavior patterns. The term "spectrum" in autism spectrum disorder refers to a wide range of symptoms and severity.
Autism spectrum disorder encompasses conditions that were previously considered independent, such as autism, Asperger`s syndrome, childhood disintegrative disorder, and an unspecified form of pervasive developmental disorder. Some people still use the term "Asperger`s syndrome" which is generally considered to be in the mild end stage of autism spectrum disorder.
Autism spectrum disorder begins in early childhood and eventually causes problems coping with society, for example in social situations, at school, and at work. Children usually have symptoms of autism in the first year. A small number of children appear to develop normally in the first year and then go through a regression period between 18 and 24 months of age when symptoms of autism appear.
While there is no cure for autism spectrum disorders, early and intensive treatment can make a big difference in the lives of many children.

Some children show signs of autism spectrum disorder in early childhood, such as decreased eye contact, lack of response when called by name, or indifference to caregivers. Other children may develop normally during the first few months or years of life, but then suddenly become introverted or aggressive or lose the language skills they had acquired. In general, signs are seen by 2 years.
Autism spectrum disorders are likely to have a pattern of behavior and severity unique to each child, ranging from low to high functioning.
Some children with autism spectrum disorders have learning difficulties and some show signs of lower than normal intelligence.
Other children with this disorder have normal to high intelligence, learn quickly, although they have problems communicating, applying what they know in daily life, and adapting to social situations.
Due to the unique combination of symptoms each child exhibits, it can sometimes be difficult to determine the severity.
In general, it is based on the level of impairment and how it affects the ability to function.

A child or adult with autism spectrum disorder may have problems with social interaction and communication skills, including any of the following signs:
Does not respond to their name or sometimes does not seem to hear you
Resists hugs and caresses; moreover, it seems that he prefers to play alone and withdraws into his own world
Does not usually make eye contact and lacks facial expression
Does not speak or has delayed speech development, or loses the ability to say words or sentences
You cannot have or start a conversation, or perhaps start one just to ask for something or name items
Speaks in an abnormal tone or rhythm and may use a singsong voice or speak like a robot
Repeats verbatim words or phrases, but doesn`t understand how to use them
Doesn`t seem to understand simple questions or prompts
Does not express emotions or feelings and seems to be unaware of the feelings of others
Does not point to or bring objects to share interests
Approaches social interactions inappropriately by behaving in a passive, aggressive, or disruptive manner
Has difficulty recognizing non-verbal cues, such as interpreting other people`s facial expressions, body postures, or tone of voice.

A child or adult with autism spectrum disorder may have limited and repetitive interests, activities, or patterns of behavior, and may even have any of the following signs:
Performs repetitive movements, such as swinging, twirling, or flapping with your hands
Do activities that could harm you, such as biting or hitting your head
Develops specific routines or rituals and alters with minimal change
Has trouble with coordination or shows strange movement patterns, such as being clumsy or walking on tiptoe, and shows strange, stiff, or exaggerated body language
Is dazzled by the details of an object, such as the spinning wheels in a toy car, but does not understand the general purpose or function of the object
It is more sensitive than usual to light, sound or physical contact, but can be indifferent to pain or temperature
Does not participate in imitation or pretend games
Obsessing over an object or activity with abnormal intensity or concentration
Has specific food preferences, such as eating only a few foods or not eating foods with a certain texture
As they mature, some children with autism spectrum disorders socialize more with other people and show fewer behavioral disturbances.
Some, usually those with less severe problems, can eventually lead normal or near normal lives. However, others continue to have difficulties with language or social skills, and in the teenage years, their behavioral and emotional problems may worsen.
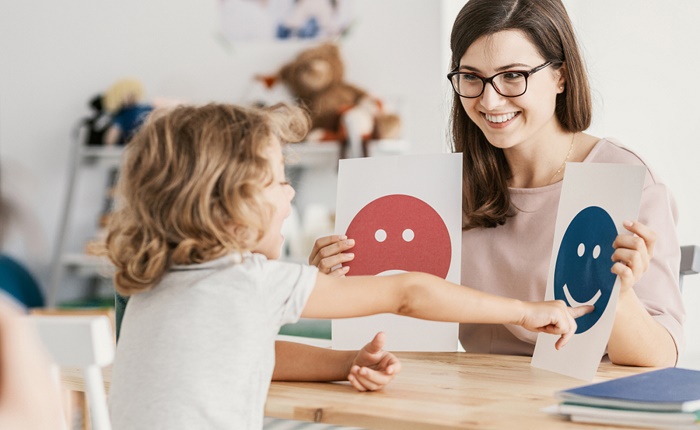

Each baby develops at their own pace, and many do not follow the exact timeline found in some parenting books. However, children with autism spectrum disorders do not usually show signs of developmental delay before the age of 2 years.
If you are concerned about your child`s development or suspect that she may have autism spectrum disorders, discuss your concerns with your doctor. The symptoms of these disorders can also be linked to other developmental disorders.
The signs of autism spectrum disorder usually appear in the early stages of development when there are obvious delays in language skills and social interactions.
Your doctor may recommend developmental tests to determine a possible delay in your child`s cognitive, language, and social skills if:
Does not respond with a smile or a happy expression at 6 months or earlier
Does not imitate sounds or facial expressions at 9 months or earlier
Does not babble or gurgle at 12 months or earlier
Does not make gestures, such as pointing or greeting, at 14 months or earlier
Does not speak simple words at 16 months or earlier
Does not play "pretend" or copycat games at or before 18 months
Does not speak two-word phrases at 24 months or earlier
Lose language or social skills at any age.
Publication Date: 2020-07-10
Source: Mayoclinic.org, Assistant professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School: Dr. Martha Herbert
.png)
.png)
.jpeg)
.png)






Ideal for small companies that need productive modules, 10 corporate emails, 5 sections, 20 product catalog, 5 SEO campaigns, e-commerce.

Ideal to start your presence on the internet, catalog of 5 products, updating documents, hosting, corporate emails and more!

Ideal for small companies that need productive modules, 10 corporate emails, 5 sections, 20 product catalog, 5 SEO campaigns, e-commerce.

Ideal to start your presence on the internet, catalog of 5 products, updating documents, hosting, corporate emails and more!